Articles
13.09.2024
How do we determine the age of a fossil? How many thousands or millions of years ago did the discovered organism live? How do we identify the geological period to which a formation belongs? Geologists and paleontologists use two primary dating methods: relative and absolute. The relative method is quicker but less precise, while the absolute method requires laboratory analysis to examine the find. By understanding the decay rate of certain isotopes and how much they have decayed, we can accurately determine the age of an organism or, more often, the rock in which it was found.
15.11.2025
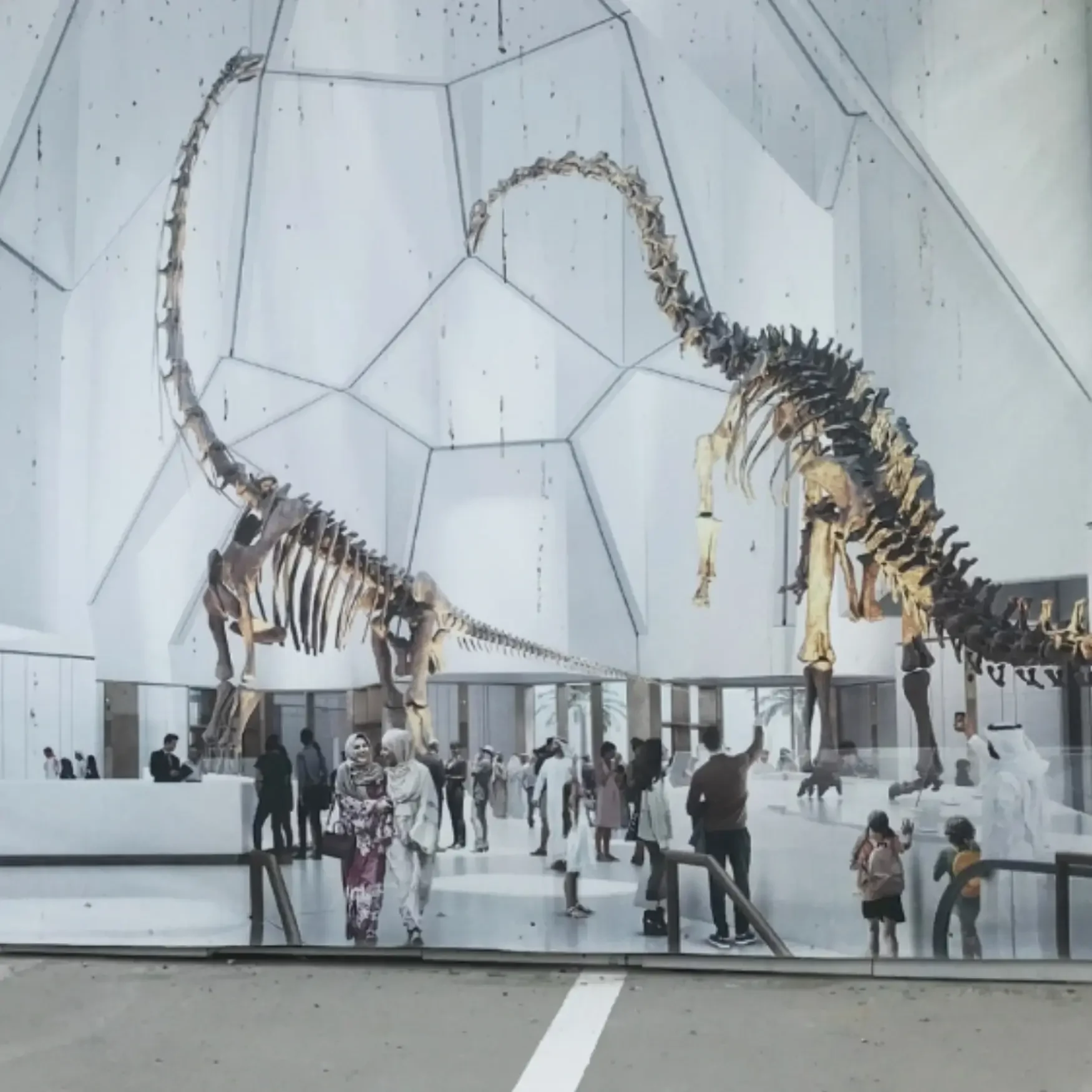
The Natural History Museum Abu Dhabi, opening on 22 November 2025 in the Saadiyat Cultural District, will be the largest of its kind in the region and a new global destination for science, nature, and education. Spanning 35,000 square metres, the museum offers an immersive journey through 13.8 billion years of natural history — from the Big Bang to the evolution of life on Earth. Highlights include Stan, the world-famous Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton, a 25-metre blue whale specimen, and the Murchison Meteorite containing 7-billion-year-old stardust.
13.09.2024
How Big Was Megalodon and How Much Did It Weigh?
Megalodon (Carcharocles megalodon, meaning “big tooth”) was the largest predatory shark in Earth’s history. Estimating the size of this prehistoric fish has been attempted numerous times. In 1909, when the first reconstruction of Megalodon’s jaw was made, scientists estimated the shark’s body length to be around 30 meters. However, today’s advances in vertebrate biology and new discoveries of Megalodon remains have halved these initial estimates. Depending on the method used to study the predator’s teeth, we get body lengths ranging from 13 to 18 meters. It was only in 2015, after studying a large sample of teeth, that an average length of 10 meters and a maximum length of 15 meters were determined. For comparison, the great white shark can theoretically reach seven meters in length. Megalodon’s size approaches that of the largest marine reptiles of the Mesozoic, such as mosasaurs and ichthyosaurs.
14.09.2024
What comes to mind when most people think of the Ice Age? It’s often imagined as an endless polar night, a frigid wilderness, and a barren snow-covered landscape stretching to the horizon. In short, it’s not the most hospitable environment for a diverse array of life.
There are contemporary examples of such harsh conditions. We have Arctic deserts, where even lichens and mosses struggle to form a continuous cover. Frozen gravel, boulders, ice as hard as stone, and stone as cold as ice dominate these lands. Even polar bears, the iconic wanderers of the Arctic, are reluctant to venture into these barren territories.
Further south lies the tundra, with its permafrost, vast marshlands, a carpet of mosses, and clusters of shrubs. Here, the soil is thin and infertile, and the landscape is characterized by high humidity. This is the domain of lichens, mosses, low-growing grasses, berries, and dwarf trees. The fauna of the tundra is limited: reindeer, arctic foxes, lemmings, hares, and wolves. There are more birds than mammals, and more fish in the cold, oxygen-rich lakes than there are birds.
14.09.2024
One of the defining characteristics of mammals is their highly developed dental system. While we can marvel at the dental “batteries” of hadrosaurs and Triceratops or discuss the differentiation of teeth in theropods and mosasaurs, it is among our mammalian relatives that we find the most remarkable variety in the form, size, and function of teeth.
Sharp, self-sharpening incisors of rodents or the impressive tusks of elephants are so familiar that they hardly elicit surprise. However, there are mammals whose enormous canines consistently raise questions—these are the sabertooth cats.
Discovered by paleontologists in the mid-19th century, sabertooth cats quickly became the epitome of a “killing machine.” The image of a beast armed with saber-like fangs, capable of taking down a mammoth, has endured in popular culture and remains prevalent in artistic depictions. On the other hand, a recent trend of “debunking” everything has also targeted these animals. Critics argue that the canines were too fragile and likely broke during bites, suggesting that sabertooth cats couldn’t hunt large prey and instead scavenged on soft tissues, using their long canines mainly for display during mating.